A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
Government set price floors and price ceilings.
These price floors and price ceilings are used to help manage scarce resources and protect buyers and sellers.
This is usually done to protect buyers and suppliers or manage scarce resources during difficult economic times.
It is an implicit tax on producers and an implicit subsidy to consumers.
However a price ceiling and price floor can also result in some inefficiencies in the marketplace.
However price floor has some adverse effects on the market.
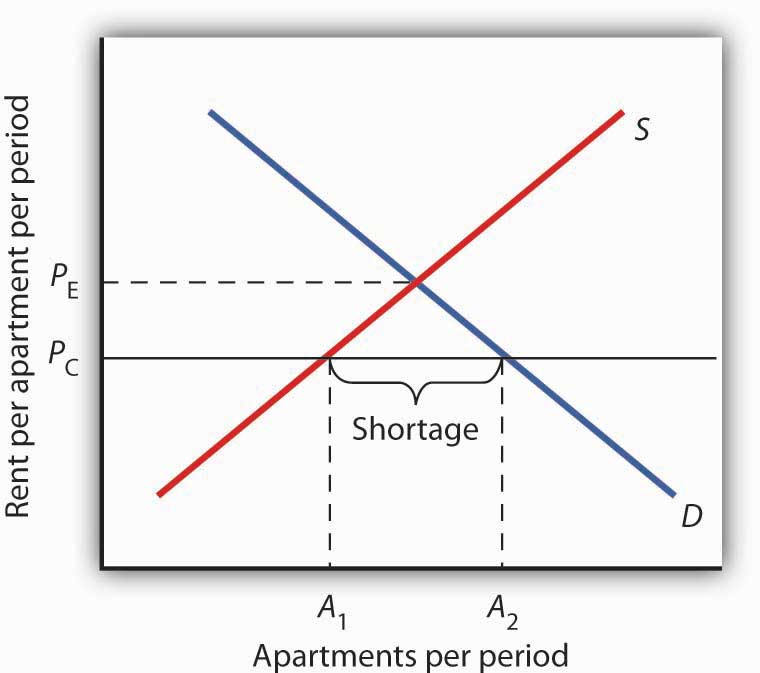
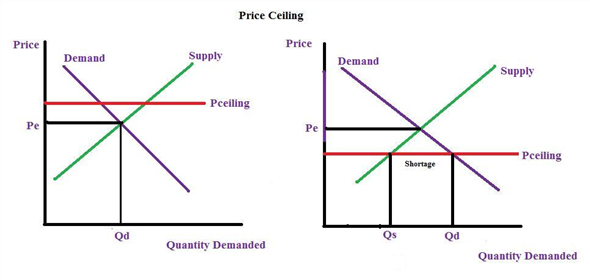
A price ceiling that is set below the equilibrium price creates a shortage that will persist.
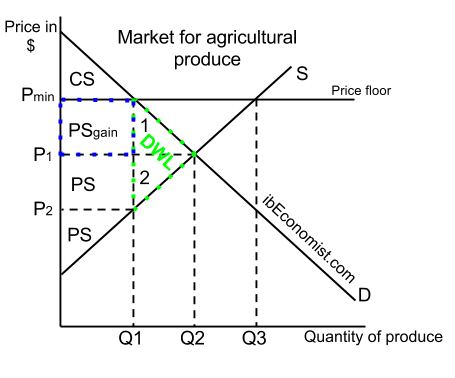
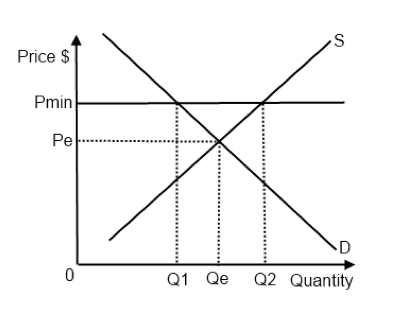
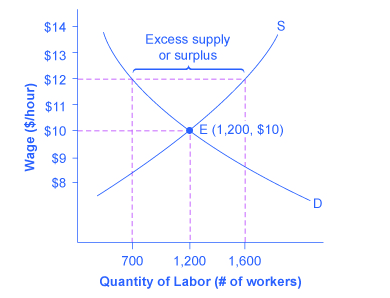
A price floor is a government set price above equilibrium price.
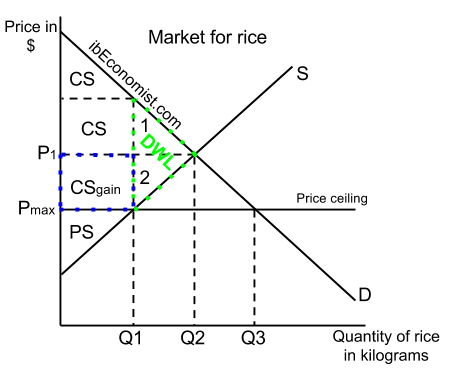
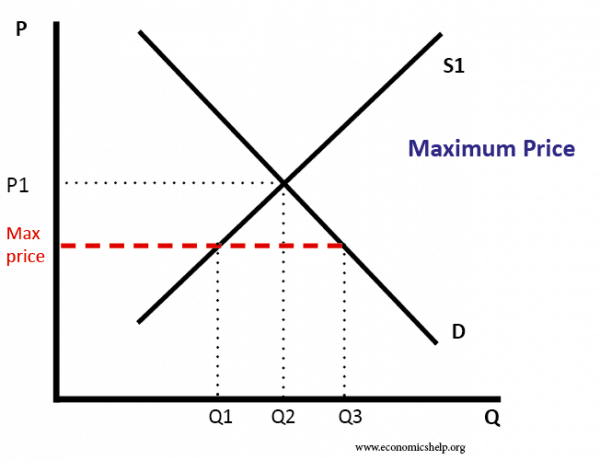
Price ceiling a price ceiling is a government set price below market equilibrium price.
This is the currently selected item.
A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
Suppose the government sets the price of an apartment at p c in figure 4 10 effect of a price ceiling on the market for apartments.
The effect of government interventions on surplus.
Taxes and perfectly inelastic demand.
Price floor is enforced with an only intention of assisting producers.
Taxation and dead weight loss.
Price ceilings and price floors.
Government set price floor when it believes that the producers are receiving unfair amount.
Price ceilings are maximum prices set by the government for particular goods and services that they believe are being sold at too high of a price and thus consumers need some help purchasing them.
A price ceiling that is set below the equilibrium price creates a shortage that will persist.
Government enforce price floor to oblige consumer to pay certain minimum amount to the producers.
Notice that p c is below the equilibrium price.
Price ceilings only become a problem when they are set below the market equilibrium price.
Price and quantity controls.
Price floors and price ceilings often lead to unintended consequences.
The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.
Example breaking down tax incidence.
Effect of price floor.
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price quantity supplied will exceed quantity demanded and excess supply or surpluses will result.
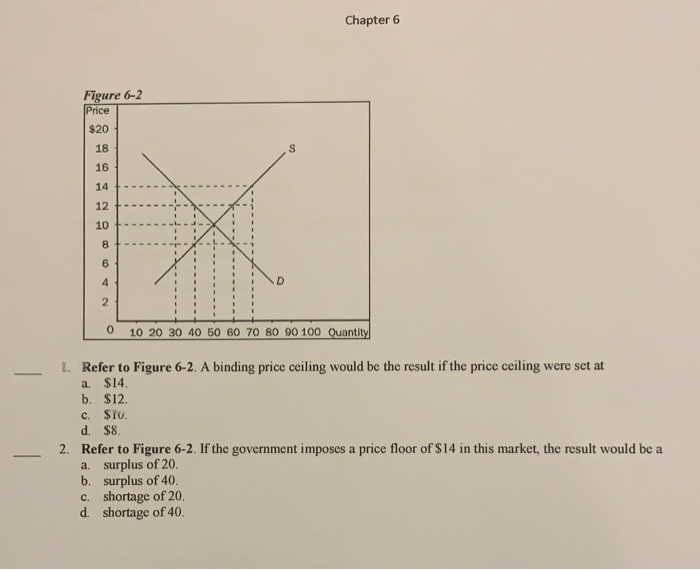
Do these create shortages or surpluses.
Percentage tax on hamburgers.
Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level.
With a price ceiling the government forbids a price above the maximum.
With a price ceiling the government forbids a price above the maximum.