Price floor is enforced with an only intention of assisting producers.
Government set price floor.
Price floors are also used often in agriculture to try to protect farmers.
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
A price floor that is set above the equilibrium price creates a surplus.
Taxation and dead weight loss.
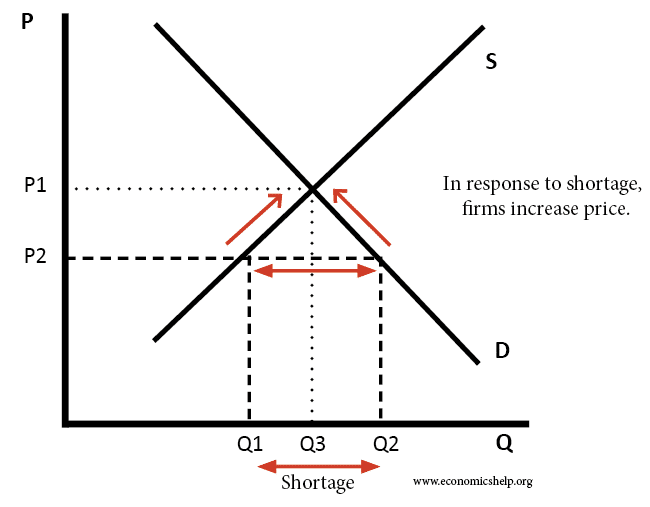
Price ceiling a price ceiling is a government set price below market equilibrium price.
B quantity supplied will increase.
Government set price floor when it believes that the producers are receiving unfair amount.
A price floor if set above the market equilibrium price means consumers will be forced to pay more for that good or service than they would if prices were set on free market principles.
Types of price controls.
A price ceiling is a type of price control usually government mandated that sets the maximum amount a seller can charge for a good or service.
If the government imposes a price floor in the market at a price of 0 40 per pound.
Minimum prices prices can t be set lower but can be set above.
Limiting price increases in a privatised.
Figure 4 8 price floors in wheat markets shows the market for wheat.
Notice that p f is above the equilibrium price of p e.
Government price controls are situations where the government sets prices for particular goods and services.
The most common price floor is the minimum wage the minimum price that can be payed for labor.
C there will be a shortage of apples.
The effect of government interventions on surplus.
How price controls reallocate surplus.
Percentage tax on hamburgers.
However price floor has some adverse effects on the market.
A quantity demanded will decrease.
A price floor is the lowest legal price a commodity can be sold at.
Price floors are used by the government to prevent prices from being too low.
A price floor is a government set price above equilibrium price it is a tax on consumers and a subsidy to producers.
This is the currently selected item.
Price floors transfer consumer surplus to producers.
Price ceilings and price floors.
Suppose the government sets the price of wheat at p f.
A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
If price floor is less than market equilibrium price then it has no impact on the economy.
Maximum price limit to how much prices can be raised e g.
Price and quantity controls.
Buffer stocks where government keep prices within a certain band.
Example breaking down tax incidence.
Minimum wage and price floors.